Fungal acne, known as pittosporum folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast on the skin. This yeast typically resides on our skin but can cause infection when hair follicles are damaged or blocked. For an in-depth look at Malassezia yeast, visit this site.
Addressing Malassezia yeast infection is crucial for preventing further skin damage, avoiding misdiagnosis, reducing recurrence risk and enhancing overall skin health.
Preventative Measures for Addressing Fungal Acne
When it comes to dealing with yeast-induced acne, taking prompt action is essential for safeguarding your skin’s well-being and preventing any potential complications. By addressing this condition diligently, you can protect your skin from further damage, reduce the risk of misdiagnosis, lower the chances of recurrence, and improve your overall skin health. Prioritizing these preventative measures offers a comprehensive approach to managing Yeast overgrowth and ensuring the best possible outcomes for your skin.
Understanding Fungal Acne
Fungal Acne vs. Regular Acne
- Fungal Acne: Caused by Malassezia yeast infecting hair follicles, resulting in small, itchy pimples, often with a red ring around them. It commonly affects the upper back, chest, and shoulders.
- Regular Acne: Caused by blocked follicles due to dead skin, oil, and bacteria. It may present as blackheads, whiteheads, pustules, nodules, or cysts and is usually less itchy.
Pittosporum Folliculitis
- Pittosporum Folliculitis: A type of folliculitis caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast. It can persist despite antibiotic treatment and is common in hot, humid climates or among individuals with oily skin or certain medical conditions.
Types of Folliculitis
- Superficial Bacterial Folliculitis: Caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria in damaged hair follicles.
- Viral Folliculitis: Associated with herpes virus or molluscum contagiosum.
- Gram-Negative Bacterial Folliculitis: Linked to Pseudomonas aeruginosa from contaminated water.
- Demodex Folliculitis: Caused by Demodex mites, affecting individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Eosinophilic Folliculitis: Often seen in HIV-positive individuals or those undergoing chemotherapy.
- Pseudofolliculitis Barbae: Also known as razor bumps, caused by ingrown hairs.
Identifying Fungal Acne
- Appearance: Small, red bumps or pustules, usually 1 to 2 mm in size, that are itchy and appear in clusters. Commonly found on the forehead, upper chest, and back.
- Difference from Regular Acne: Regular acne caused by yeast features a variety of lesions like blackheads, cysts, and pustules, which are less itchy compared to yeast acne.
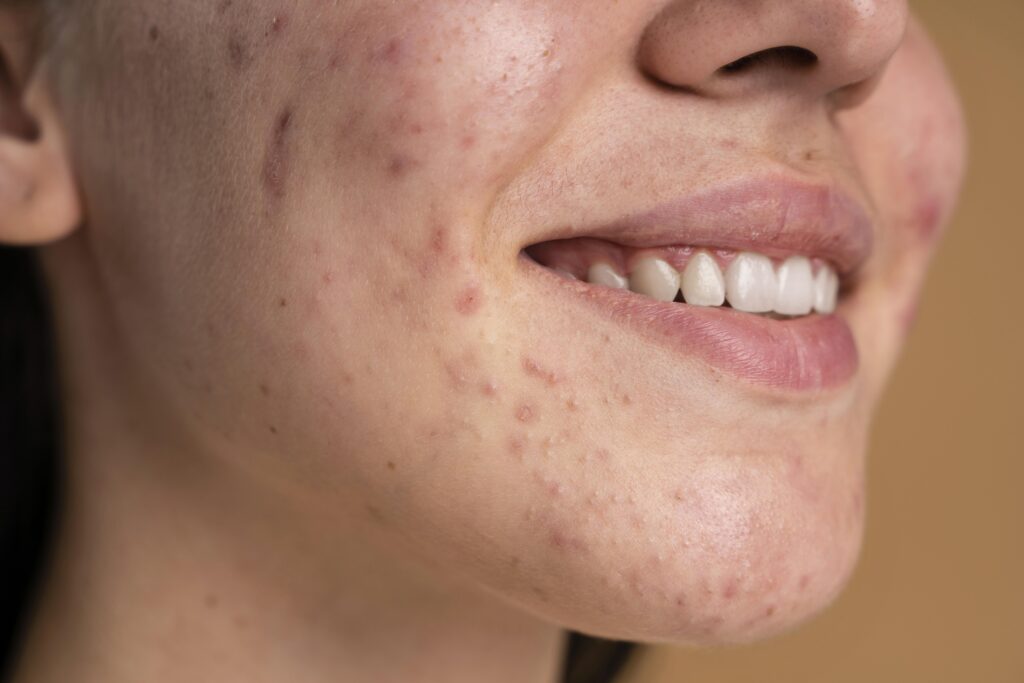
How to Treat Fungal Acne
- Antifungal Creams: Apply directly to affected areas to target the yeast infection.
- Antifungal Washes: Use to cleanse and reduce yeast on the skin’s surface.
- Antifungal Tablets: Prescribed for more severe infections to manage internally.
Note: Fungal acne may recur, so ongoing maintenance treatment may be necessary.
For more skincare products that may help, read our guide on Best Skincare Products in Korea.
How to prevent Fungal Acne:
1. Shower and Change Clothes: It is important to shower and change clothes immediately after workouts to remove sweat and bacteria from the skin. This helps in preventing the growth of fungi that can lead to yeast infection
2. Careful Grooming: When shaving or waxing, take care to avoid nicks and cuts that can create openings for fungal infections. Using clean, sharp tools and following proper grooming techniques can help reduce the risk of fungal acne.
3. Clean Hot Tubs: If you use hot tubs, ensure they are well-maintained and cleaned regularly. Proper maintenance helps to prevent the proliferation of fungi and bacteria in the water, which can cause skin issues, including yeast infection.
4. Wash Swimwear: After swimming, it is important to thoroughly rinse and dry swimwear to remove any lingering moisture. Damp clothing can create an environment for fungi to thrive, so ensuring swimwear is clean and dry helps in preventing fungal acne.
5. Wear Loose Clothing: In hot, humid conditions or during exercise, wearing loose-fitting clothing allows the skin to breathe and reduces friction, which can help prevent acne caused by yeast. Tight clothing can trap sweat and moisture, creating an environment for fungal growth.
6. Use Dandruff Shampoo: Applying dandruff shampoo a few times a week, especially during breakouts, can help control fungal growth on the scalp and skin. Look for shampoos containing antifungal ingredients like ketoconazole or zinc pyrithione.
7. Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports overall skin health. Consuming foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of fungal acne.
FAQs
To manage fungal acne at home, apply antifungal creams or shampoos that contain ketoconazole or selenium sulfide to address the yeast responsible for the infection. Keep the affected areas clean with antifungal cleansers and avoid tight clothing to minimize sweating and irritation. Also, maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to overall skin health.
Since fungal acne isn’t linked to oil production, applying salicylic acid alone won’t resolve the issue. You need to specifically target the yeast overgrowth on your skin to reduce this effectively.
Using Vaseline, also known as slugging, is not recommended for treating fungal acne and may even worsen it for some people. However, Vaseline can be beneficial for addressing other skin issues like injuries, chafing, or dry skin.
Fungal acne can leave scars, similar to other types of acne. Factors such as shaving, waxing, or taking antibiotics for other conditions can contribute to the imbalance that leads to fungal acne. Fortunately, there are treatment options available that can help reduce scarring.
Oral Antifungal Medications such as Itraconazole — This antifungal capsule is effective for treating infections in various parts of the body, including the fingernails, toenails, lungs, mouth, throat, and more.

